夜间灯光遥感是能够探测夜间微光的光学遥感技术,已被证明可以直观地反映人类社会经济活动差异,但是其社会经济感知机制以及应用过程与影响效应仍不清晰。施开放副教授研究小组长期聚焦于城市化进程中人类社会经济活动的多维表征,发展了面向夜间灯光遥感的环境影响过程与效应分析的理论与方法,近期取得了部分研究进展如下。
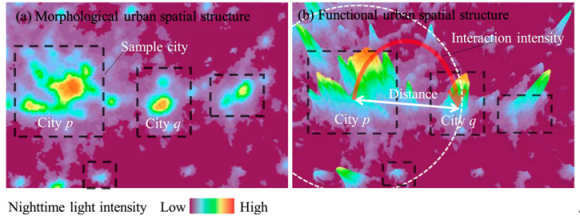
阐明了城市空间结构对碳排放影响的人口规模条件效应,揭示了形态与功能多中心城市空间结构对碳排放的影响差异。研究成果分别以What urban spatial structure is more conducive to reducing carbon emissions? A conditional effect of population size和Differentiated effects of morphological and functional polycentric urban spatial structure on carbon emissions in China: An empirical analysis from remotely sensed nighttime light approaches为题发表于应用地理学领域顶级学术期刊Applied Geography(SSCI JCR一区,TOP期刊)以及地球信息科学领域主流学术期刊International Journal of Digital Earth(SCI一区,TOP期刊)。
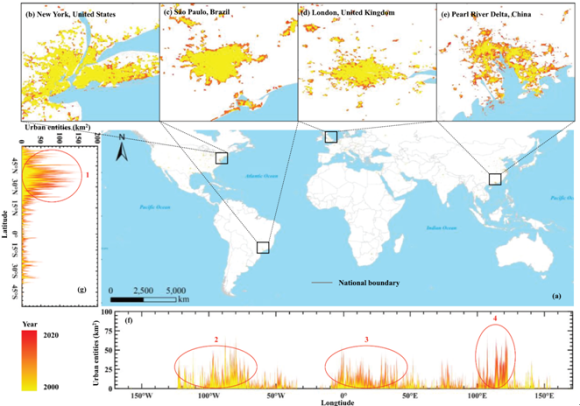
绘制与分析了全球城市实体时空动态变化,并进一步定量评估了郊区绿化与郊区化对地表城市热岛强度的影响。研究成果分别以Mapping and evaluating global urban entities (2000–2020): A novel perspective to delineate urban entities based on consistent nighttime light data和Suburban greening and suburbanization changing surface urban heat island intensity in China为题发表于遥感与地理信息科学领域主流学术期刊GIScience and Remote Sensing(SCI一区(基础版),TOP期刊)以及城市建筑与环境领域主流学术期刊Building and Environment(SCI一区,TOP期刊)。
以上论文均以必赢优惠y272net为第一完成单位,施开放为论文的第一或通讯作者,相关论文链接如下:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0143622822002260;
https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2023.2176558;
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/15481603.2022.2161199;
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360132322011362。